Introduction: Nigeria’s Energy Transformation Imperative
Nigeria faces critical energy challenges that impact economic development, business operations, and quality of life across the nation. Furthermore, unreliable power supply costs Nigerian businesses an estimated ₦2.4 trillion annually through downtime, generator fuel expenses, and equipment damage. However, smart energy systems Nigeria implementations offer transformative solutions through IoT connectivity and intelligent energy management.
Smart energy systems leverage IoT devices, sensors, and data analytics to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption. Moreover, these systems enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated control reducing waste while improving reliability. Subsequently, Nigerian businesses implementing smart energy solutions report 35-45% reduction in energy costs while enhancing operational sustainability.
The convergence of renewable energy technologies, IoT connectivity, and intelligent control systems creates unprecedented opportunities for Nigerian energy transformation. Additionally, universal SIM technology from providers like Genyz Solutions enables reliable communication between distributed energy devices across challenging African telecommunications infrastructure. Therefore, smart energy systems represent essential infrastructure for Nigeria’s sustainable development goals and economic competitiveness.
This comprehensive guide explores smart energy systems Nigeria applications, implementation strategies, and the connectivity solutions enabling successful deployments across diverse Nigerian operational environments from Lagos commercial districts to remote northern agricultural operations.
1. What Are Smart Energy Systems?
Defining Intelligent Energy Infrastructure
Smart energy systems represent integrated networks of energy generation, storage, distribution, and consumption devices connected through IoT technology enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and automated control. Furthermore, these systems combine hardware components including sensors, smart meters, controllers, and communication devices with software platforms analyzing data and optimizing energy performance.
Unlike traditional energy infrastructure operating with limited visibility and manual control, smart energy systems provide comprehensive real-time data about energy flows throughout facilities or networks. Moreover, this visibility enables identification of inefficiencies, prediction of maintenance requirements, and automated optimization reducing costs while improving reliability.
The core components of smart energy systems include energy generation sources (solar panels, wind turbines, generators), storage systems (batteries, capacitors), distribution infrastructure (smart grids, microgrids), consumption devices (HVAC systems, lighting, equipment), and monitoring/control systems connected through cellular IoT Nigeria networks.
Technology Foundation
Smart energy systems rely on several integrated technologies working together. Subsequently, IoT sensors measure energy generation, consumption, voltage, current, power quality, and environmental conditions. These sensors connect to gateways or modems equipped with roaming SIMs enabling data transmission across Nigerian telecommunications networks.
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) provides granular energy consumption data at device, circuit, or facility levels. Additionally, this detailed information enables identification of energy waste and optimization opportunities invisible to traditional utility meters providing only aggregate monthly readings.
Control systems receive data from sensors and meters, analyze information using sophisticated algorithms, and automatically adjust operations optimizing energy efficiency. Furthermore, machine learning capabilities enable continuous improvement as systems learn from operational patterns and outcomes.
Cloud-based management platforms aggregate data from distributed devices, provide visualization through dashboards and reports, and enable remote management of energy systems. Moreover, mobile applications extend control capabilities to facility managers and decision-makers regardless of location.
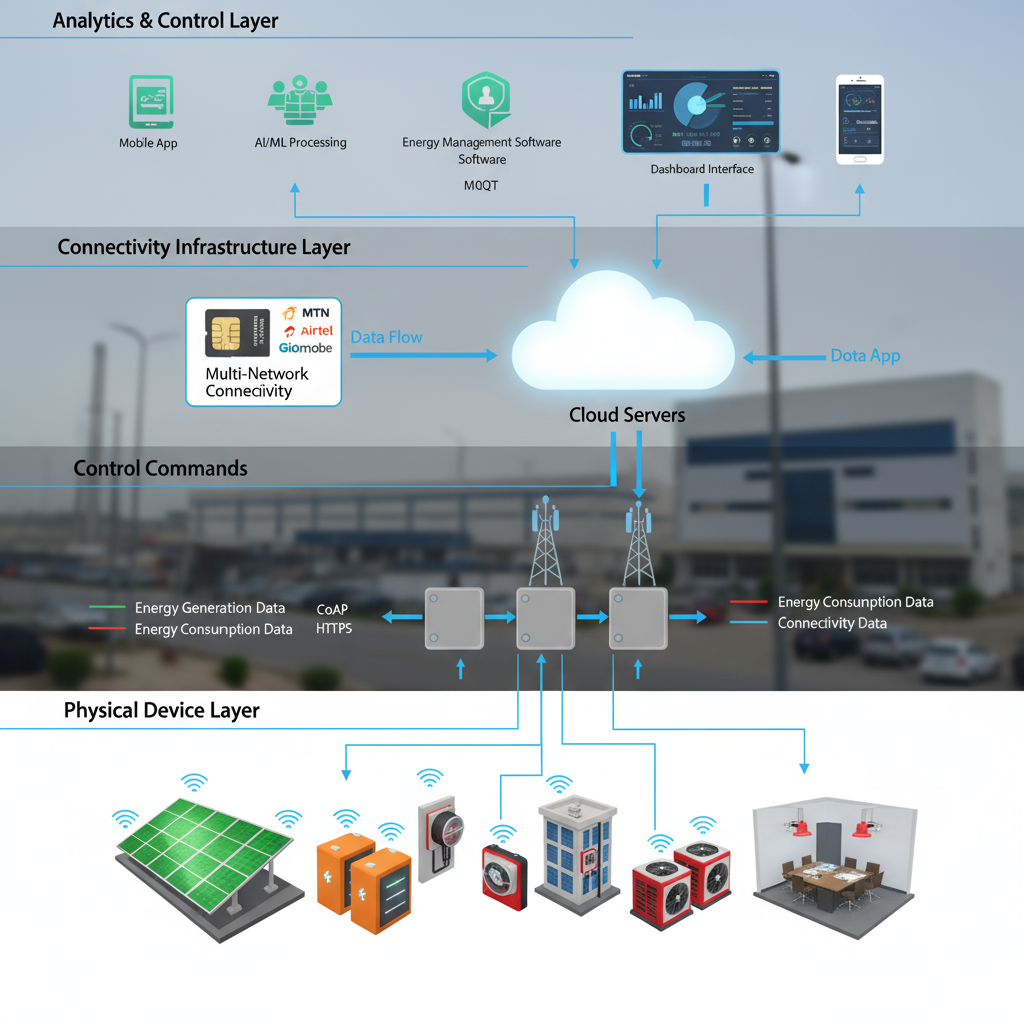
2. Smart Energy Systems for Sustainable Future
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Smart energy systems deliver dual benefits of environmental sustainability and economic performance making them essential for Nigeria’s development trajectory. Furthermore, these systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions through optimized energy efficiency, integration of renewable sources, and elimination of waste from inefficient operations.
Nigerian businesses implementing comprehensive smart energy systems report 40-60% reduction in carbon emissions while simultaneously achieving 35-50% decrease in energy costs. Moreover, these improvements enhance corporate sustainability profiles increasingly important for international partnerships, export markets, and investor relations.
These systems enable integration of distributed renewable energy sources including rooftop solar installations, small wind turbines, and biogas generators. Subsequently, businesses reduce dependence on unreliable grid power and expensive diesel generators while supporting Nigeria’s renewable energy transition goals.
Resilience and Energy Security
Smart energy systems improve resilience through diversified energy sources, intelligent storage management, and automated load balancing during grid disruptions. Furthermore, this proves particularly valuable in Nigeria where power supply inconsistency significantly impacts business operations and competitiveness.
Microgrids enabled by smart energy technology can operate independently during grid outages while seamlessly reconnecting when utility power restores. Additionally, battery storage systems charged during low-demand periods or from renewable sources provide backup power eliminating dependence on diesel generators.
Energy storage optimization algorithms maximize battery lifespan while ensuring adequate capacity for critical operations during outages. Moreover, predictive analytics anticipate grid disruptions enabling proactive preparations minimizing operational impacts.
Supporting Nigeria’s Development Goals
Nigeria’s Economic Recovery and Growth Plan emphasizes energy sector reform and renewable energy adoption as critical development priorities. Furthermore, smart energy systems directly support these objectives through improved efficiency, renewable integration, and grid modernization.
The Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission increasingly recognizes smart energy technology as essential infrastructure for achieving reliable, affordable, sustainable energy access. Subsequently, regulatory frameworks continue evolving to facilitate rather than hinder smart energy deployments across public and private sectors.
3. Smart Energy Control Systems for Sustainable Buildings
Building Energy Management Systems
Smart energy control systems for sustainable buildings integrate HVAC, lighting, security, and power management into unified platforms optimized for energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Furthermore, these building management systems (BMS) leverage IoT connectivity monitoring and controlling distributed devices throughout facilities.
Nigerian commercial buildings implementing comprehensive BMS report 30-45% energy consumption reduction compared to traditional control approaches. Moreover, improved indoor environmental quality enhances worker productivity and satisfaction creating additional value beyond direct energy savings.
Occupancy sensors detect room usage patterns automatically adjusting lighting, temperature, and ventilation based on actual occupancy rather than fixed schedules. Additionally, this eliminates energy waste in unoccupied areas while maintaining comfort in active spaces.
Integrated Control Strategies
Advanced control algorithms optimize building energy performance through coordinated management of multiple systems. Subsequently, thermal storage strategies pre-cool buildings during off-peak electricity periods reducing consumption during expensive peak hours.
Daylight harvesting systems automatically dim artificial lighting when natural light provides adequate illumination. Furthermore, motorized blinds coordinate with lighting controls optimizing daylight utilization while managing solar heat gain affecting cooling loads.
Demand response capabilities enable buildings to reduce consumption during grid stress periods or high electricity price periods. Moreover, automated load shedding prioritizes critical operations while temporarily reducing non-essential consumption supporting grid stability and reducing costs.
Nigerian Implementation Examples
A Lagos commercial complex partnered with Genyz Solutions implementing comprehensive smart building systems across 85,000 square meters of office and retail space. Furthermore, universal SIM connectivity ensured reliable communication between distributed control devices and central management platforms.
The implementation reduced annual energy costs by ₦67 million while improving tenant satisfaction scores 34%. Additionally, real-time monitoring enabled rapid identification and resolution of equipment issues preventing costly system failures and comfort complaints.
Banks including FCMB and Wema Bank deploy smart building systems across branches optimizing energy usage while maintaining reliable environmental control for data centers and customer areas. Moreover, these systems reduced branch energy costs 40% while improving operational reliability.
4. Smart Energy Systems Examples in Nigeria
Manufacturing Operations
Nigerian manufacturing facilities deploy smart energy systems optimizing production equipment, compressed air systems, process heating, and facility infrastructure. Furthermore, these implementations deliver significant cost savings while improving production efficiency and equipment reliability.
A Kaduna textile manufacturer implemented comprehensive energy monitoring across production lines using cellular IoT connectivity from Genyz Solutions. Subsequently, the system identified inefficient motor operations, compressed air leaks, and process optimization opportunities delivering ₦23 million annual savings.
Real-time power quality monitoring protects sensitive production equipment from voltage fluctuations and harmonics common in Nigerian electrical infrastructure. Moreover, automated load management prevents demand charges by intelligently scheduling non-critical operations avoiding peak consumption periods.
Agricultural Applications
Nigerian farms leverage smart energy systems managing irrigation pumps, grain drying equipment, cold storage, and facility operations. Furthermore, solar-powered systems with battery storage and IoT monitoring enable reliable energy access in remote areas lacking grid connections.
A large farming operation across Plateau State deployed smart energy management for 48 irrigation pump systems. The universal SIM connectivity ensured reliable monitoring despite challenging rural network coverage. Additionally, the system reduced energy costs 52% through solar integration and optimized pump scheduling.
Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze equipment performance data identifying developing issues before failures occur. Subsequently, this prevents costly crop losses from irrigation system failures during critical growing periods.
Commercial and Hospitality Sector
Hotels, shopping centers, and office buildings implement smart energy systems managing diverse electrical loads including HVAC, lighting, elevators, kitchens, and laundry facilities. Furthermore, these systems coordinate energy usage optimizing costs while maintaining service quality and customer experience.
A Nigerian hotel chain across Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt deployed comprehensive energy management achieving ₦34 million annual savings across 12 properties. Moreover, improved energy efficiency enhanced corporate sustainability credentials attracting environmentally conscious corporate clients and international partnerships.
5. Smart Energy Management Technologies
Advanced Metering Infrastructure
Smart meters form the foundation of energy management providing granular consumption data at intervals ranging from seconds to minutes rather than monthly manual readings. Furthermore, this detailed information enables precise identification of energy waste and verification of efficiency improvement initiatives.
Nigerian utilities increasingly deploy smart meters supporting improved billing accuracy, theft detection, and demand forecasting. Additionally, businesses implementing private smart metering gain operational insights unavailable from utility meters providing only aggregate facility consumption.
Sub-metering at circuit or equipment levels identifies specific energy waste sources invisible in facility-level data. Subsequently, this enables targeted interventions addressing actual problems rather than implementing broad efficiency measures with uncertain impacts.
Energy Storage Systems
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) enable load shifting, backup power, and renewable energy integration maximizing value from smart energy investments. Furthermore, lithium-ion battery costs declined 85% over the past decade making storage economically viable for Nigerian applications.
Storage systems charged during low-demand periods or from renewable sources provide power during expensive peak periods or grid outages. Moreover, intelligent charge/discharge management algorithms optimize battery utilization while extending service life.
Integration with solar installations enables energy independence reducing reliance on unreliable grid power and expensive diesel generators. Additionally, battery systems provide instantaneous backup power eliminating service interruptions affecting sensitive equipment or critical operations.
IoT Connectivity Infrastructure
Reliable connectivity between distributed energy devices and management platforms proves essential for smart energy system success. Furthermore, Nigerian deployments require multinetwork SIM solutions from providers like Genyz Solutions ensuring consistent communication across diverse operational environments.
Universal SIM technology enables automatic switching between MTN, Airtel, Glo, and 9mobile networks based on coverage and performance. Subsequently, this multi-carrier capability ensures reliable data transmission from remote locations with variable network coverage.
Low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies including NB-IoT and LTE-M provide energy-efficient connectivity for battery-powered sensors requiring years of operational life. Moreover, these technologies support massive device deployments at costs enabling comprehensive monitoring across large facilities or distributed operations.
6. Nigeria’s Smart Energy Journey and Future Path
Current State of Development
Nigeria has made significant progress implementing smart energy technologies despite infrastructure and regulatory challenges. Furthermore, private sector deployments led by forward-thinking businesses demonstrate technical feasibility and economic benefits encouraging broader adoption.
The Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission developed frameworks supporting distributed generation, net metering, and renewable energy integration. Additionally, these regulatory developments create favorable conditions for smart energy system deployments across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors.
Lagos State leads Nigerian smart energy adoption through pilot programs, regulatory support, and infrastructure investments. Moreover, other states including Abuja FCT, Rivers, and Kano increasingly recognize smart energy importance for economic development and sustainability goals.
Barriers and Opportunities
High upfront investment costs deter some Nigerian businesses from implementing smart energy systems despite strong ROI potential. Furthermore, limited awareness of technology capabilities and benefits prevents many organizations from exploring smart energy opportunities.
Financing mechanisms including partnerships with banks like FCMB and Wema Bank provide payment flexibility making smart energy investments accessible to broader business segments. Additionally, demonstrated success stories encourage hesitant organizations to pursue similar implementations.
Skills gaps in smart energy system design, installation, and maintenance constrain deployment pace. Subsequently, training programs and partnerships with experienced providers like Genyz Solutions address expertise limitations enabling successful implementations.
Strategic Recommendations
Nigeria should prioritize smart grid infrastructure investments improving reliability while enabling integration of distributed renewable generation and storage. Furthermore, enhanced grid infrastructure benefits all energy users while supporting economic development and sustainability objectives.
Regulatory frameworks should continue evolving supporting innovation while ensuring safety, reliability, and consumer protection. Moreover, streamlined approval processes for renewable installations and storage systems accelerate adoption supporting national development goals.
Public-private partnerships can accelerate smart energy deployment through shared investment, technology transfer, and capability development. Additionally, government demonstration projects showcase technology benefits encouraging private sector adoption.
7. Implementation Guide for Nigerian Businesses
Assessment and Planning
Successful smart energy system implementation begins with comprehensive energy audits identifying consumption patterns, inefficiencies, and optimization opportunities. Furthermore, detailed analysis establishes baseline performance enabling accurate measurement of improvement benefits.
Businesses should evaluate energy costs, reliability challenges, sustainability goals, and growth projections informing smart energy investment decisions. Additionally, analysis should consider available renewable energy resources, facility characteristics, and operational requirements.
Technology Selection
Choosing appropriate smart energy technologies requires evaluation of specific operational needs, budget constraints, and technical capabilities. Furthermore, Nigerian deployments must account for power quality challenges, network coverage variations, and environmental conditions affecting system performance.
Connectivity infrastructure selection proves critical for system success. Therefore, universal SIM solutions from Genyz Solutions provide optimal reliability through automatic multi-network switching ensuring consistent communication across diverse Nigerian locations.
Deployment Best Practices
Phased implementation reduces risk while enabling learning and optimization. Furthermore, initial deployments in representative facilities validate technology performance and economic benefits before organization-wide expansion.
Professional installation ensures proper system integration, configuration, and testing. Additionally, comprehensive commissioning verifies all components function correctly and achieve specified performance levels.
Training programs prepare operational teams managing smart energy systems, interpreting data, and responding to alerts. Moreover, ongoing technical support from providers ensures issues receive prompt resolution while system optimization continues throughout operational lifecycle.
Conclusion: Powering Nigeria’s Sustainable Future
Smart energy systems Nigeria implementations represent essential infrastructure for businesses pursuing operational excellence, cost reduction, and sustainability goals. Furthermore, the technology delivers measurable benefits including 35-50% energy cost reduction, improved reliability, and enhanced environmental performance.
Success requires partnering with connectivity providers combining technical expertise with deep understanding of Nigerian telecommunications infrastructure and energy management challenges. Moreover, Genyz Solutions offers universal SIM connectivity, comprehensive technical support, and proven experience supporting successful IoT deployments across Nigeria and Africa.
Transform Your Energy Management Today
Contact Genyz Solutions for comprehensive consultation on smart energy systems implementation, universal SIM connectivity solutions, and IoT deployment strategies tailored to your Nigerian operations.

