Introduction
Tech infrastructure investment is reshaping global digital landscapes. Major technology companies now commit billions to data centers. Additionally, they invest in AI computing facilities and cloud infrastructure. For instance, Microsoft announced over $15 billion in UAE investments. These investments span 2023 to 2029. Primarily, the focus is AI data center expansion.
Consequently, this illustrates massive capital requirements. Modern digital services demand substantial infrastructure. For Nigerian businesses and African technology leaders, these patterns reveal critical insights. Specifically, they show infrastructure priorities and technology trends. Furthermore, they demonstrate connectivity foundations enabling digital transformation.
Meanwhile, Nigeria may not attract Microsoft-scale investments immediately. However, understanding these drivers helps African organizations make informed decisions. Therefore, they can plan technology infrastructure effectively. Similarly, they can evaluate connectivity solutions strategically. Moreover, they can develop digital strategies ensuring competitiveness. This matters particularly in an AI-powered global economy.
This analysis examines Microsoft’s UAE investment strategy. Additionally, it explores implications for African digital transformation. Furthermore, it reveals how Nigerian businesses can leverage global technology trends. Specifically, through strategic infrastructure planning and reliable connectivity solutions. Whether you’re planning data center investments or evaluating cloud services, understanding these trends proves essential. Consequently, your technology strategy aligns with global developments. At the same time, it addresses unique African market characteristics.
1. Understanding Microsoft’s $15 Billion UAE Strategy
Microsoft’s substantial UAE commitment reveals strategic considerations. These apply to any organization planning significant technology infrastructure investments. Moreover, Nigerian businesses can adapt these lessons to local contexts.
AI Data Centers: The Core Investment
Computing Infrastructure for AI Demands
Microsoft Vice Chair Brad Smith confirmed key investment details. Specifically, the largest share of $15.2 billion focuses on AI data centers. These expand across the UAE. Moreover, the facilities house thousands of GPU processors. These are specialized chips designed for AI computation. Consequently, they enable cloud-based AI services. Additionally, they support machine learning model training. Finally, they power intelligent applications serving global customers.
The investment includes securing advanced Nvidia chips. Furthermore, it requires U.S. export licenses. Specifically, this includes 21,500 equivalent Nvidia A100 GPUs. The previous administration approved these. Additionally, 60,400 A100-equivalent chips were cleared. These involve more advanced GB300 GPUs. The current administration approved these. These chips represent cutting-edge AI computing technology.
Meanwhile, each facility requires massive infrastructure. Specifically, this includes power infrastructure and cooling systems. Additionally, it requires network connectivity supporting continuous operation.
For Nigerian technology leaders, this illustrates AI’s infrastructure intensity. Admittedly, local businesses won’t build GPU-scale data centers. However, the same principle applies. Specifically, AI-powered services require robust underlying infrastructure. This includes reliable connectivity and sufficient computing resources. Furthermore, it requires dependable power supplies. These are challenging considerations in African operating environments.
Strategic Geographic Positioning
Why the UAE Attracts Tech Investment
Several factors make the UAE attractive for Microsoft’s infrastructure investment. First, government support proves critical. UAE leadership prioritizes becoming a global AI hub. Consequently, they provide regulatory frameworks and financial incentives. Additionally, they facilitate strategic partnerships supporting technology company expansion.
Second, geographic location matters significantly. The UAE sits between Europe, Africa, and Asia. Therefore, UAE data centers serve multiple regional markets. Moreover, they provide acceptable latency for cloud services.
Third, stable infrastructure attracts investment. Specifically, the UAE offers reliable power and telecommunications. Additionally, physical infrastructure supports demanding data center operations.
Finally, diplomatic relations facilitate technology transfer. Close US-UAE relationships simplify export licenses. Furthermore, they enable strategic partnerships requiring government approval.
Nigerian policymakers can learn from this approach. Notably, countries attracting substantial technology investment provide stable regulatory environments. Additionally, they ensure infrastructure reliability. Furthermore, they offer strategic government support. In contrast, tax incentives or cheap labor alone prove insufficient.
Partnership and Compliance Considerations
Navigating Geopolitical Technology Concerns
Microsoft’s investment includes strategic partnerships. Specifically, a $1.5 billion stake in Abu Dhabi AI company G42. Consequently, this provides board representation through Brad Smith. However, G42’s past ties to China attracted scrutiny. Specifically, Washington expressed concerns about Beijing accessing advanced semiconductors. This could occur through third parties like the UAE.
Nevertheless, Smith noted G42 made “enormous progress.” Specifically, implementing systems complying with U.S. law. These address advanced chip access and technology transfer. This geopolitical dimension affects technology infrastructure investments globally. Therefore, companies must navigate competing interests. Additionally, they must address export controls. Furthermore, they consider strategic concerns beyond pure business calculations.
For Nigerian businesses partnering with international technology providers, similar considerations apply. Specifically, understanding regulatory requirements proves essential. Additionally, addressing data sovereignty concerns matters. Furthermore, recognizing geopolitical factors affecting technology access ensures success. Consequently, partnerships succeed rather than encounter unexpected compliance challenges.
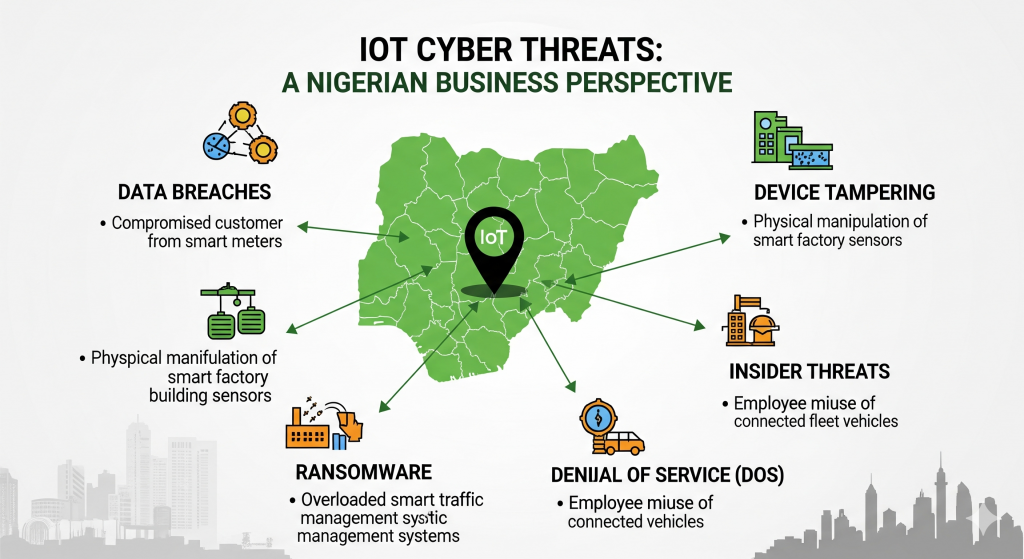
2. Implications for African Digital Infrastructure Development
Microsoft’s UAE investment reveals broader trends. These affect African technology development. Furthermore, they influence digital transformation strategies. Therefore, Nigerian businesses should understand and incorporate them into planning.
The AI Infrastructure Gap
Africa’s Computing Capacity Challenge
Global AI development requires massive computing infrastructure. Specifically, this includes thousands of GPUs and petabytes of storage. Additionally, it requires high-bandwidth network connectivity. Currently, Africa lacks substantial AI computing infrastructure. In comparison, North America, Europe, and Asia possess extensive facilities. Moreover, the Middle East increasingly develops capacity.
This gap creates dependencies. Specifically, African businesses developing AI applications rely on distant data centers. Consequently, this introduces latency. Additionally, it raises data sovereignty concerns. Furthermore, it creates ongoing operational costs paid to foreign providers. For instance, Nigerian AI startups train models using AWS or Azure. However, these facilities are located in Europe or the US.
Nevertheless, this gap also presents opportunities. Countries establishing AI infrastructure across Africa gain first-mover advantages. Therefore, they serve rapidly growing markets. Notably, South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria possess the market scale. Additionally, they have technical talent. Furthermore, they maintain infrastructure foundations potentially supporting regional data centers. Consequently, these could serve African customers effectively.
Cloud Dependency vs. Local Infrastructure
Strategic Decisions for Nigerian Businesses
Microsoft’s UAE investment targets specific customer needs. Specifically, those requiring low-latency cloud services. Additionally, customers need AI computing resources unavailable through distant data centers. Similarly, Nigerian businesses face comparable considerations. Therefore, they must choose between building local infrastructure and relying on international cloud providers. Alternatively, they adopt hybrid approaches balancing both strategies.
Cloud Services Benefits: First, no capital expenditure for infrastructure. Second, instant access to cutting-edge technology. Third, elastic scaling matching business growth. Finally, professional management and security.
Local Infrastructure Advantages: First, lower latency for Nigerian customers. Second, data sovereignty and regulatory compliance. Third, reduced long-term operational costs. Finally, local job creation and capacity building.
Currently, most Nigerian businesses adopt cloud-first strategies. This occurs due to limited capital. Additionally, technical expertise requirements for infrastructure management prove challenging. However, as digital operations mature, alternatives emerge. Specifically, hybrid approaches incorporating local infrastructure become economically viable. Furthermore, they prove strategically valuable.
Connectivity as Foundation
Why Reliable Networks Matter for Infrastructure Investment
Whether organizations build local infrastructure or rely on cloud services, reliable connectivity remains fundamental. Specifically, data centers require multiple redundant network connections. Consequently, this ensures continuous operation. Similarly, cloud-dependent businesses need reliable internet access. Therefore, service availability is maintained.
Nigeria’s telecommunications landscape creates both challenges and opportunities. Specifically, multiple operators provide varying coverage. These include MTN, Airtel, Glo, and 9mobile. Additionally, reliability differs across operators. Therefore, organizations requiring mission-critical connectivity deploy multinetwork solutions. These automatically switch between operators. Consequently, they maintain connectivity based on availability and performance.
GenYZ Solutions’ universal SIM cards enable Nigerian businesses to maintain reliable connections. These support cloud services, data center operations, and distributed digital infrastructure. Moreover, they function regardless of individual operator performance. Therefore, this proves critical as organizations scale digital operations.
3. Technology Export Controls and African Access
Microsoft’s need for U.S. export licenses highlights important dimensions. Specifically, these affect technology access globally. Furthermore, they impact African markets.
Understanding Export Control Frameworks
How Advanced Technology Access Is Regulated
U.S. export controls restrict advanced semiconductor technology exports. Specifically, they prevent adversary nations from accessing strategic capabilities. These controls particularly affect AI chips. For instance, Nvidia’s H100 and GB300 GPUs enable training large AI models.
Countries seeking access must demonstrate several things. First, strong diplomatic relations with technology-exporting nations. Second, robust compliance frameworks preventing unauthorized transfer. Third, end-use verification ensuring technology serves stated purposes. Finally, alignment with Western technology governance standards.
The UAE obtained necessary licenses through specific means. Specifically, diplomatic relationships proved essential. Additionally, compliance commitments mattered. Furthermore, strategic alignment with U.S. interests facilitated approval. Similarly, African nations seeking technology access face comparable requirements.
African Technology Sovereignty Considerations
Balancing Access with Independence
Export controls create technology dependency. Specifically, African organizations accessing cutting-edge AI chips rely on foreign government approval. Similarly, cloud services require such approval. Consequently, this dependency raises strategic concerns. Particularly regarding technology sovereignty and economic independence.
Some African technology leaders advocate developing indigenous alternatives. Therefore, this reduces dependency on Western or Chinese technology platforms. However, building competitive semiconductor manufacturing proves challenging. Similarly, AI chip design capabilities require decades of investment. Additionally, expertise development exceeds most African nations’ current resources.
Pragmatic approaches balance leveraging available technology with building local capabilities. Specifically, through partnerships and compliance while gradually developing expertise. Therefore, focus on areas where Africa can compete globally. For instance, software development and data science applications. Additionally, industry-specific solutions rather than semiconductor manufacturing.
Opportunities Through Partnerships
How Nigerian Businesses Access Advanced Technology
Rather than waiting for local AI chip manufacturing, Nigerian businesses access advanced technology differently. Specifically, through several channels.
Cloud Platforms: Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud provide API access. Therefore, businesses use GPUs and AI services. Moreover, this requires no physical hardware ownership.
Technology Partnerships: Collaborations with international providers bring expertise. Additionally, they provide infrastructure access to African markets.
Regional Data Centers: Supporting establishment of West African facilities proves valuable. Specifically, operated by global providers serving regional customers.
Open Source Alternatives: Leveraging open-source AI models and tools proves effective. Consequently, this reduces dependency on proprietary platforms. Furthermore, it eliminates export license requirements.
GenYZ Solutions facilitates these strategies effectively. Specifically, by providing reliable connectivity enabling Nigerian businesses to access international cloud services. Additionally, supporting hybrid infrastructure deployments. Furthermore, maintaining communications with global technology partners. Therefore, these prove essential for organizations navigating complex technology access landscapes.
4. Lessons for Nigerian Infrastructure Investment
Microsoft’s UAE commitment offers practical lessons. Nigerian businesses, investors, and policymakers can apply these. Specifically, when planning technology infrastructure investments.
Start with Demand Assessment
Understanding Actual Requirements
Microsoft’s investment responds to demonstrated demand. Specifically, for AI and cloud services across the Middle East region. Notably, the company isn’t speculatively building capacity. Instead, it’s expanding infrastructure meeting existing needs. Additionally, it addresses projected customer requirements.
Nigerian infrastructure investors should similarly assess actual demand. Specifically, through several approaches.
Market Research: First, survey potential customers. Therefore, understand their technology requirements. Additionally, identify budget constraints. Furthermore, clarify service expectations.
Competitive Analysis: Evaluate existing infrastructure capacity. Additionally, identify underserved segments. Furthermore, locate geographic areas lacking adequate services.
Growth Projections: Develop realistic forecasts based on several factors. Specifically, digital transformation trends and economic growth. Additionally, technology adoption patterns.
Pilot Projects: Test demand through small-scale deployments. Consequently, this occurs before committing to large infrastructure investments.
Too often, African infrastructure investments rely on aspirational projections. In contrast, they should use demonstrated market demand. Otherwise, this results in underutilized facilities. Furthermore, it creates poor investment returns.
Prioritize Reliability Over Scale
Quality Before Quantity
Nigeria doesn’t need Microsoft-scale data centers immediately. However, existing infrastructure must operate reliably. Specifically, this includes consistent power and redundant connectivity. Additionally, professional management and security meeting customer expectations.
A small but highly reliable data center proves more valuable. Specifically, one serving Nigerian businesses effectively. In comparison, a large facility experiencing frequent outages proves problematic. Similarly, security breaches destroy value. Furthermore, connectivity problems undermine trust. Building reputation for reliability attracts customers. Moreover, it justifies premium pricing. In contrast, unreliability destroys trust regardless of capacity or features.
This principle applies beyond data centers. Specifically, Nigerian businesses deploying any technology infrastructure must prioritize operational reliability. For instance, retail systems, banking platforms, and logistics networks. GenYZ Solutions’ multinetwork SIM cards embody this philosophy. Specifically, ensuring reliable connectivity across varying network conditions. Therefore, rather than promising maximum theoretical speeds, they deliver consistent availability.
Plan for Power Infrastructure
Addressing Nigeria’s Energy Challenges
Data centers consume enormous electricity. For instance, Microsoft’s UAE facilities require megawatts of continuous power. Similarly, Nigerian infrastructure investments must address power reliability challenges. Specifically, through several approaches.
On-Site Generation: Diesel or natural gas generators provide backup. Specifically, during grid outages.
Solar Integration: Renewable energy reduces operational costs. Additionally, it decreases grid dependency.
Efficient Cooling: Tropical climates increase cooling requirements. However, modern designs minimize power consumption.
Battery Storage: This smooths transitions between power sources. Consequently, it prevents equipment damage during switches.
These considerations apply to all Nigerian digital infrastructure. Specifically, not just data centers. For instance, banking systems, telecommunications equipment, and IoT deployments. All require power planning accounting for grid unreliability.
Develop Local Technical Talent
Building Sustainable Operations
Microsoft’s UAE investment includes training programs. Specifically, developing local talent managing AI infrastructure. Consequently, this capacity building ensures sustainable operations. Furthermore, it extends beyond the technology company’s direct involvement.
Nigerian infrastructure investments should similarly prioritize skills development. Specifically, through several mechanisms.
Training Programs: Educating engineers on infrastructure management proves essential. Additionally, covering security and optimization.
University Partnerships: Collaborating with Nigerian institutions develops relevant curricula. Furthermore, it supports research programs.
Certification Programs: Supporting staff obtaining internationally recognized credentials demonstrates expertise.
Knowledge Transfer: Ensuring expatriate experts transfer skills to Nigerian colleagues proves critical. Therefore, this avoids creating permanent dependencies.
5. Connectivity Solutions Enabling Infrastructure Success
Regardless of infrastructure scale, reliable connectivity remains fundamental. Specifically, to success. GenYZ Solutions provides multinetwork connectivity Nigerian businesses need. Therefore, supporting digital operations across sectors.
Multinetwork Redundancy for Critical Operations
Why Single-Network Solutions Fail
Data centers, cloud services, and digital infrastructure require continuous connectivity. However, single-network approaches create vulnerabilities. Specifically, when that operator experiences outages, entire operations become compromised. Similarly, coverage gaps create problems. Furthermore, performance degradation affects business.
Universal SIM cards from GenYZ Solutions automatically switch between networks. Specifically, MTN, Airtel, Glo, and 9mobile. Moreover, switching occurs based on availability and performance. Consequently, this redundancy ensures several benefits.
Business Continuity: Operations continue despite individual network problems.
Geographic Coverage: Connectivity maintains as staff or equipment moves. Specifically, between areas with varying operator coverage.
Performance Optimization: Automatic selection of networks providing best current performance.
Cost Management: Intelligent routing of traffic based on pricing. Additionally, considering data caps.
For Nigerian businesses operating critical infrastructure, multinetwork connectivity proves essential. Specifically, whether banking systems supported by FCMB and Wema Bank partnerships, logistics networks, or manufacturing facilities. Therefore, this becomes mandatory rather than optional.
Supporting Hybrid Cloud Architectures
Connecting Local and Cloud Infrastructure
Many Nigerian businesses adopt hybrid approaches. Specifically, combining local infrastructure with international cloud services. However, this architecture requires reliable connectivity. Therefore, enabling several functions.
Data Synchronization: Continuous replication between local and cloud storage. Consequently, ensuring consistency. Additionally, providing disaster recovery.
Workload Distribution: Dynamic allocation of processing between local servers and cloud resources. Therefore, optimizing costs and performance.
API Communications: Applications spanning local and cloud components require stable connections. Consequently, maintaining functionality.
Remote Management: IT teams managing distributed infrastructure need reliable access. Specifically, regardless of location.
GenYZ Solutions’ SIM management platform provides centralized control. Specifically, over connectivity across hybrid deployments. Therefore, monitoring performance and managing costs. Furthermore, ensuring reliability as infrastructure scales.
Enabling IoT and Edge Computing
Distributed Infrastructure Connectivity
Modern infrastructure extends beyond centralized data centers. Specifically, it includes edge computing nodes. Additionally, IoT devices collecting data. Furthermore, providing localized processing. However, these distributed components require reliable connectivity. Particularly when operating in challenging environments.
Remote Locations: Agricultural monitoring operates in areas with marginal coverage. Similarly, oil and gas operations face challenges. Furthermore, logistics tracking encounters connectivity issues.
Mobile Equipment: Vehicle tracking requires connectivity while moving. Similarly, portable terminals need continuous connections. Additionally, mobile workers demand reliable access.
IoT Sensors: Thousands of devices transmit telemetry data. Moreover, they receive configuration updates. Furthermore, they report status continuously.
Universal SIM cards enable these deployments effectively. Specifically, by maintaining connectivity across Nigeria’s diverse geography. Additionally, across varying network landscapes. Therefore, as organizations expand digital infrastructure beyond traditional data centers, reliable multinetwork connectivity becomes increasingly critical. Consequently, this ensures operational success.
6. Investment Considerations and ROI Planning
Understanding infrastructure investment economics helps Nigerian businesses. Specifically, making informed decisions about technology spending. Furthermore, determining expected returns.
Capital vs. Operational Expenditure Models
Different Investment Approaches
Microsoft’s $15 billion UAE commitment represents capital expenditure. Specifically, purchasing land and building facilities. Additionally, acquiring equipment. Consequently, this approach provides long-term control. Furthermore, it offers potentially lower per-unit costs at scale.
In contrast, many Nigerian businesses prefer operational expenditure models. Specifically, paying monthly fees for cloud services. Additionally, for managed connectivity or hosted infrastructure. However, OpEx approaches offer several advantages.
Lower Initial Costs: No substantial upfront investment required.
Predictable Expenses: Fixed monthly costs simplify budgeting.
Flexibility: Easier scaling up or down matching business needs.
Reduced Risk: Provider absorbs technology obsolescence. Additionally, infrastructure management challenges.
Genyz Solutions’ connectivity services follow OpEx models. Moreover, with transparent Naira-based pricing. Consequently, enabling Nigerian businesses to accurately forecast costs. Furthermore, without currency fluctuation risks. Therefore, eliminating unexpected capital requirements.
Calculating Infrastructure ROI
Measuring Technology Investment Returns
Infrastructure investments should generate measurable business value. Specifically, through several mechanisms.
Revenue Enablement: Digital services create new revenue streams. Additionally, they expand existing ones.
Cost Reduction: Automation provides efficiency improvements. Similarly, resource optimization reduces operational expenses.
Risk Mitigation: Improved reliability reduces business risks. Additionally, better security prevents losses. Furthermore, compliance capabilities avoid penalties.
Competitive Advantage: Capabilities differentiate your business from competitors. Consequently, attracting customers.
Nigerian businesses evaluating infrastructure investments should develop ROI models. Specifically, projecting these benefits against total costs. These include connectivity, power, maintenance, and management expenses. Genyz Solutions assists customers with these analyses. Therefore, ensuring connectivity considerations are accurately incorporated. Consequently, into infrastructure planning.
Phased Investment Strategies
Growing Infrastructure Sustainably
Rather than attempting Microsoft-scale investments immediately, Nigerian businesses benefit from phased approaches. Specifically, following a structured progression.
Phase 1 – Foundation: Establish reliable connectivity. Additionally, basic infrastructure. Furthermore, essential services.
Phase 2 – Optimization: Improve performance. Moreover, add redundancy. Furthermore, enhance management capabilities.
Phase 3 – Expansion: Scale to additional locations. Additionally, new services. Furthermore, additional customer segments. Specifically, based on demonstrated demand.
Phase 4 – Innovation: Invest in advanced capabilities. For instance, AI, analytics, or automation. Consequently, delivering competitive advantages.
This staged approach limits financial risk. Moreover, it enables learning and adjustment. Specifically, based on actual experience. Therefore, rather than theoretical projections.
7. Future Trends in Technology Infrastructure Investment
Microsoft’s UAE commitment reflects broader trends. These shape technology infrastructure globally. Therefore, Nigerian businesses should monitor them. Furthermore, incorporating them into strategic planning.
AI-Driven Infrastructure Demand
Computing Requirements Continue Growing
AI adoption accelerates across industries. Consequently, creating unprecedented demand for computing resources. Additionally, requiring storage capacity. Furthermore, demanding network bandwidth. Specifically, organizations deploying AI require infrastructure supporting several functions.
Model Training: Computationally intensive processes develop AI algorithms. Specifically, from data.
Inference Services: Real-time AI predictions and decisions require low-latency responses.
Data Storage: Massive datasets feed AI systems. Additionally, storing results.
Network Capacity: High-bandwidth connections move data. Specifically, between storage, processing, and end users.
Nigerian businesses leveraging AI require infrastructure planning. For instance, for fraud detection, customer service, or logistics optimization. Additionally, agricultural prediction. Cloud services provide immediate access. However, as AI usage scales, hybrid approaches become attractive. Specifically, incorporating local processing. Consequently, becoming economically viable.
Edge Computing Expansion
Distributed Processing Closer to Data Sources
Rather than centralizing all processing, edge computing distributes intelligence differently. Specifically, closer to where data is generated. Additionally, where it’s consumed. Consequently, this architecture reduces latency. Furthermore, it decreases bandwidth costs. Moreover, it enables functionality during connectivity interruptions.
Nigerian infrastructure strategies should incorporate edge computing. Particularly for applications requiring real-time response. Additionally, those operating in bandwidth-constrained environments. Genyz Solutions’ multinetwork connectivity enables these distributed deployments. Specifically, maintaining communication with central systems. Moreover, providing local autonomy during network challenges.
Sustainability and Green Infrastructure
Environmental Considerations in Technology Investment
Data centers consume substantial energy. Additionally, water for cooling. However, modern investments increasingly prioritize sustainability. Specifically, through renewable energy. Furthermore, efficient cooling technologies. Moreover, carbon offset programs.
Nigeria’s abundant solar potential positions the country favorably. Specifically, for sustainable technology infrastructure. Therefore, investments incorporating renewable energy reduce operational costs. Furthermore, they meet growing customer expectations. Particularly for environmental responsibility.
Conclusion: Strategic Infrastructure Planning for Nigerian Digital Success
Tech infrastructure investment patterns illustrated by Microsoft’s $15 billion UAE commitment reveal strategic priorities. These apply to Nigerian businesses regardless of investment scale. Whether you’re planning local data center facilities or evaluating cloud services, the same principles apply. Specifically, start with demonstrated demand. Additionally, prioritize reliability over capacity. Furthermore, ensure power stability. Moreover, develop local talent. Finally, maintain multinetwork connectivity supporting operations.
Genyz Solutions provides the connectivity foundation Nigerian digital infrastructure requires. Specifically, universal SIM cards automatically switching between networks. These include MTN, Airtel, Glo, and 9mobile. Consequently, ensuring continuous operation despite individual operator challenges. Our proven experience supporting FCMB, Wema Bank, and enterprises across Nigeria demonstrates capability. Specifically, delivering reliable connectivity for mission-critical infrastructure. Therefore, where failures create unacceptable business impacts.
As global technology investment accelerates, African digital transformation progresses simultaneously. Therefore, organizations with reliable infrastructure and connectivity foundations position themselves effectively. Specifically, to compete successfully. In contrast, those struggling with unreliable systems face challenges. Similarly, poor connectivity creates barriers. Furthermore, inadequate infrastructure planning creates risks. Consequently, falling behind as competitors leverage technology for advantages.
Plan Your Infrastructure Success
Don’t let infrastructure limitations restrict your digital ambitions. Whether you’re evaluating cloud services, planning local deployments, or building hybrid architectures, reliable multinetwork connectivity from Genyz Solutions ensures success. Specifically, your technology investments deliver expected returns.
Contact Genyz Solutions today for consultation on connectivity solutions. Your digital future requires infrastructure built on reliable foundations. Start building today.