Nigeria’s IoT market is experiencing explosive growth, with projections indicating a 35% annual increase through 2027, driven by businesses in Lagos, Abuja, and emerging markets seeking digital transformation solutions. However, identifying suitable IoT devices for African network environments presents unique challenges that can make or break deployment success. Many Nigerian enterprises struggle with device compatibility issues, connectivity failures, and poor performance due to inadequate device selection processes.
The critical difference between IoT success and failure often lies in understanding what to look for when evaluating IoT devices for deployment across Nigeria’s diverse network landscape. With over 200 million mobile subscribers and varying network coverage across different regions, selecting devices that work seamlessly with roaming SIMs and multinetwork solutions becomes paramount for business success.
This comprehensive guide provides Nigerian IT managers, operations directors, and business owners with expert insights on identifying IoT devices that deliver reliable performance across challenging African telecommunications environments while maximizing return on investment through proper device connectivity management.
1. Understanding IoT Device Fundamentals in the Nigerian Context
IoT devices in Nigerian business environments must meet specific criteria that differ significantly from devices designed for developed markets with consistent network infrastructure. These connected devices require robust hardware specifications, adaptable software capabilities, and compatibility with African telecommunications standards.
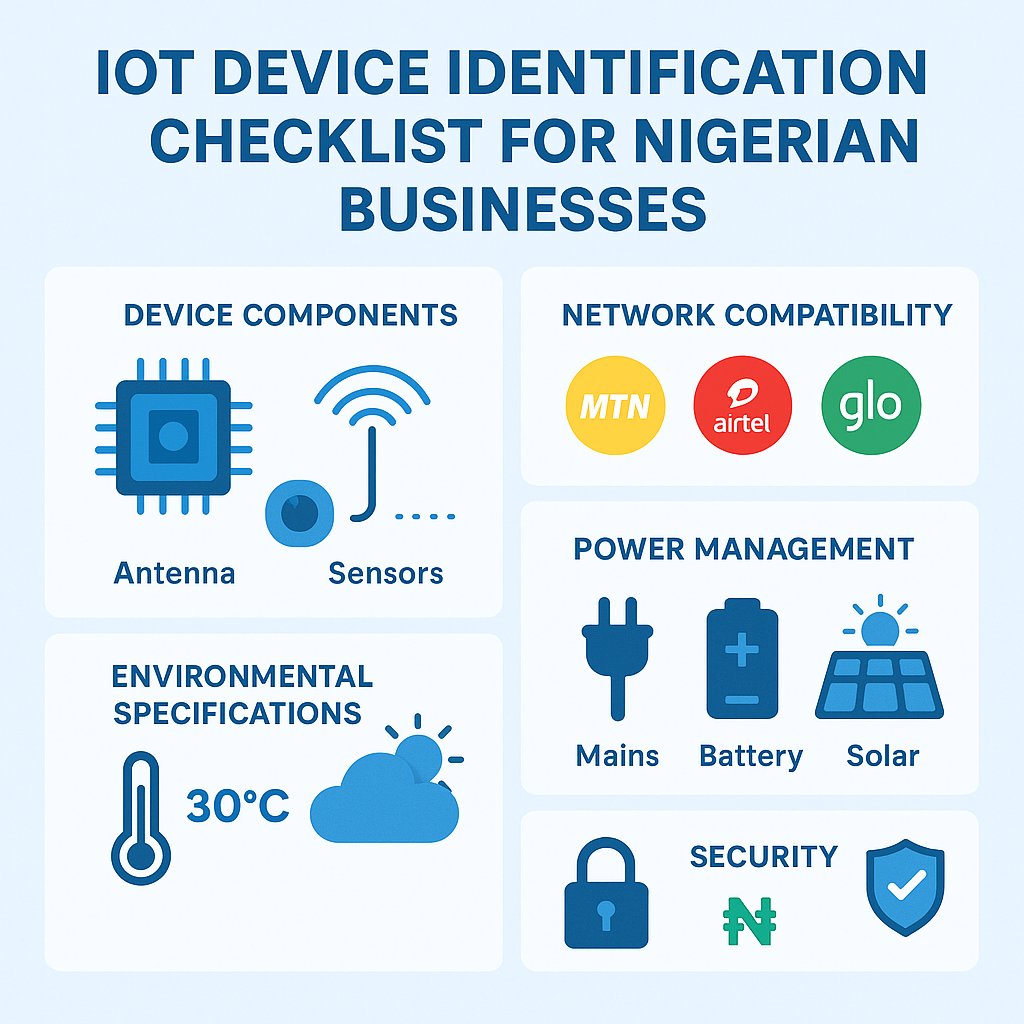
The foundation of IoT device identification begins with understanding cellular IoT Nigeria requirements. Devices must support multiple frequency bands used by Nigerian carriers including MTN (900/1800/2100 MHz), Airtel (900/1800/2600 MHz), Glo (900/1800/2100 MHz), and 9mobile (900/1800/2100/2600 MHz). This multi-band support ensures universal SIM compatibility across different network operators.
Power consumption represents another critical identification factor, as Nigerian businesses face frequent power outages and voltage fluctuations. IoT devices should feature low-power design with battery backup capabilities, typically consuming less than 5 watts during normal operation and offering 8-12 hours of backup power during outages.
Environmental resilience proves essential for African deployment conditions. Devices must withstand temperature ranges from 0°C to 60°C, humidity levels up to 95%, and dust ingress common in Nigerian industrial and outdoor environments. Look for IP65 or higher ingress protection ratings.
M2M connectivity Africa specialists recognize that device longevity significantly impacts total cost of ownership. Quality IoT devices should offer minimum 5-year operational lifespans with over-the-air update capabilities to extend functionality and security throughout their lifecycle.
2. Hardware Specifications: What Nigerian Businesses Should Look For
Identifying appropriate IoT hardware requires evaluating multiple technical specifications that directly impact performance in African network conditions. Processing power represents the foundation of device capabilities, with ARM Cortex-M series processors proving most suitable for Nigerian IoT deployments due to their power efficiency and robust performance characteristics.
Memory specifications deserve careful attention, with minimum requirements of 512KB RAM and 2MB flash storage for basic IoT applications. More complex applications requiring local data processing or temporary storage during connectivity interruptions need 2MB RAM and 8MB flash storage minimum.
Communication modules must support 2G/3G/4G LTE standards with fallback capabilities. Many rural Nigerian areas still rely on 2G networks, making backward compatibility essential. Devices should include dual-SIM capabilities for redundant connectivity using different network operators simultaneously.
Antenna design significantly impacts performance across varying Nigerian network conditions. External antenna connections provide superior flexibility for optimizing signal reception in different deployment environments. Internal antennas, while more compact, may struggle with signal quality in buildings with metal construction common in Nigerian industrial facilities.
Power management systems should include multiple input options: mains power with voltage regulation (85-265V AC to handle Nigerian power quality issues), battery backup systems, and solar charging capabilities for remote deployments. Smart power management should automatically switch between power sources while monitoring battery health.
Sensor integration capabilities determine device versatility for different Nigerian business applications. Look for devices supporting multiple sensor types through GPIO pins, analog inputs, and digital communication protocols (I2C, SPI, UART). This flexibility enables customization for specific industry requirements without hardware redesign.
3. Essential Software Attributes for African IoT Deployments
Software capabilities often determine IoT device success in challenging African network environments where connectivity interruptions are common. Device operating systems must handle intermittent connectivity gracefully while maintaining operational integrity during network transitions.
Local data storage and edge computing capabilities prove crucial for Nigerian deployments. Devices should buffer sensor data locally during connectivity outages, automatically synchronizing with cloud platforms when connections restore. This offline-first approach ensures no data loss during the frequent network interruptions common across African telecommunications infrastructure.
Over-the-air (OTA) update functionality represents a non-negotiable requirement for long-term device management. Remote monitoring solutions require secure, reliable firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities, add new features, and optimize performance without physical device access. This capability proves particularly valuable for devices deployed in remote locations across Nigeria’s diverse geography.
Security frameworks must address African-specific cyber threats while complying with Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) regulations. Look for devices supporting end-to-end encryption, certificate-based authentication, and secure boot processes. The software should include intrusion detection capabilities and automatic security patch deployment.
Protocol support determines integration flexibility with existing Nigerian business systems. Devices should support multiple communication protocols including MQTT, CoAP, HTTP/HTTPS, and proprietary protocols used by local software vendors. Multi-protocol support ensures compatibility with diverse business management systems common in Nigerian enterprises.
API accessibility enables custom integration with Nigerian business applications. Well-designed IoT devices provide RESTful APIs, webhooks, and SDK support for popular programming languages. This flexibility allows Nigerian developers to create custom applications tailored to specific business requirements.
4. Connectivity Requirements and Network Compatibility
Network compatibility represents the most critical factor for IoT device success in Nigeria’s complex telecommunications landscape. Devices must demonstrate seamless operation across multiple carrier networks while handling the frequent coverage gaps and quality variations characteristic of African network infrastructure.
Universal SIM compatibility ensures devices work optimally with roaming SIMs that automatically switch between Nigerian network operators. Look for devices certified for use with major Nigerian carriers and supporting automatic network selection based on signal strength and data costs. This capability prevents connectivity interruptions when traveling between regions with different dominant carriers.
Data consumption optimization becomes crucial given the higher data costs in Nigerian markets compared to developed economies. Efficient devices should compress data transmissions, batch communications to minimize connection overhead, and support configurable transmission intervals based on application requirements and connectivity costs.
Latency tolerance mechanisms help devices perform effectively despite the higher latency common in African network infrastructure. Real-time applications may struggle, but devices with intelligent buffering and adaptive communication protocols can maintain functionality despite network delays.
Multi-carrier connectivity support through dual-SIM functionality provides redundancy essential for mission-critical applications. Primary SIM cards handle normal operations while secondary SIMs activate during coverage gaps or primary network failures. This approach ensures maximum uptime across Nigeria’s diverse network coverage areas.
Band aggregation capabilities enable devices to combine multiple frequency bands simultaneously, improving data speeds and connection reliability. This technology proves particularly valuable in Lagos IoT deployment scenarios where network congestion affects individual band performance during peak usage periods.
5. Industry-Specific IoT Device Applications in Nigeria
Nigerian businesses across different industries require IoT devices with specialized capabilities tailored to sector-specific operational requirements. Understanding these applications helps identify appropriate devices for particular business contexts while ensuring optimal performance and return on investment.
Banking sector IoT implementations, including partnerships with institutions like FCMB and Wema Bank, require devices with enhanced security features, tamper detection, and regulatory compliance capabilities. ATM monitoring devices need cellular backup connectivity, environmental sensors for cabinet conditions, and secure communication protocols meeting Central Bank of Nigeria requirements.
Agricultural IoT applications demand rugged devices capable of operating in harsh environmental conditions common across Nigerian farming regions. Soil monitoring sensors must withstand moisture, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure while providing reliable data transmission from remote locations with limited network coverage. Solar power capabilities prove essential for off-grid deployments.
Manufacturing sector devices require integration with existing industrial control systems while providing predictive maintenance capabilities. Vibration sensors, temperature monitors, and machine health diagnostic tools must communicate through industrial protocols while maintaining cybersecurity standards appropriate for sensitive production environments.
Logistics and transportation applications need GPS-enabled devices with real-time tracking capabilities, geofencing functionality, and driver behavior monitoring. These devices must operate reliably during long-distance transportation across Nigeria’s diverse terrain while providing accurate location data and vehicle diagnostics.
Healthcare IoT devices require strict compliance with patient privacy regulations while providing reliable monitoring of medical equipment and environmental conditions. Temperature monitoring for pharmaceutical storage, equipment tracking in hospitals, and patient monitoring devices need redundant connectivity and fail-safe operational modes.
6. Evaluation Criteria: Selecting the Right IoT Devices for Your Business
Systematic evaluation of IoT devices requires establishing clear criteria aligned with Nigerian business operational requirements and budget constraints. This structured approach ensures optimal device selection while avoiding costly deployment mistakes common in African IoT implementations.
Total cost of ownership analysis should encompass initial device costs, connectivity expenses, maintenance requirements, and expected operational lifespan. Nigerian businesses must evaluate device pricing in Naira terms while considering currency fluctuation impacts on ongoing operational costs. Quality devices with higher upfront costs often provide better long-term value through reduced maintenance and longer operational life.
Vendor support capabilities prove crucial for successful long-term operations. Evaluate suppliers’ Nigerian presence, local technical support availability, replacement part accessibility, and documentation quality in English. International vendors without local presence may struggle to provide timely support during critical operational issues.
Certification and compliance verification ensures devices meet Nigerian regulatory requirements and international quality standards. Look for NCC type approval, FCC/CE certifications, and industry-specific compliance certificates. These certifications indicate proper testing and regulatory approval for Nigerian deployment.
Scalability considerations determine whether devices can accommodate business growth and changing requirements. Modular designs allow functionality expansion without complete device replacement, while cloud-based management platforms enable efficient scaling across multiple locations as businesses expand throughout Nigeria and other African markets.
Integration complexity affects deployment timelines and costs. Devices with comprehensive documentation, developer tools, and pre-built integrations with popular business software reduce implementation time and technical risk. Consider available technical expertise within your organization when evaluating integration requirements.
Performance benchmarking against similar devices helps identify optimal solutions for specific applications. Request performance data for Nigerian network conditions, including connection success rates, data throughput, and power consumption under various operational scenarios.
7. Future-Proofing Your IoT Device Selection Strategy
The rapidly evolving African telecommunications landscape requires IoT device selection strategies that anticipate future technological developments and changing business requirements. Forward-thinking device evaluation ensures long-term investment protection and operational continuity.
5G network expansion across major Nigerian cities will create opportunities for more sophisticated IoT applications requiring higher bandwidth and lower latency. While current deployments may focus on 4G LTE compatibility, selecting devices with 5G upgrade paths or modular communication modules ensures future compatibility without complete hardware replacement.
Edge computing capabilities will become increasingly important as African network infrastructure improves and data processing requirements grow. Devices with sufficient processing power and memory for local analytics and machine learning inference will provide competitive advantages through reduced cloud dependencies and faster response times.
Artificial intelligence integration at the device level will enable predictive maintenance, automated optimization, and intelligent decision-making without constant cloud connectivity. Look for devices with AI acceleration capabilities or sufficient processing power for machine learning inference algorithms.
Regulatory evolution by the Nigerian Communications Commission and other African regulatory bodies may introduce new requirements for IoT devices. Selecting devices from manufacturers with strong compliance track records and update capabilities helps ensure continued regulatory compliance as requirements evolve.
Environmental sustainability considerations will increasingly influence device selection as Nigerian businesses adopt green technology initiatives. Energy-efficient devices with recyclable components and extended operational lifespans align with corporate sustainability goals while reducing long-term environmental impact.
Conclusion and Implementation Recommendations
Successfully identifying and selecting IoT devices for Nigerian business deployments requires balancing technical specifications, operational requirements, and cost considerations while accounting for unique African infrastructure challenges. The key factors include network compatibility across multiple carriers, environmental resilience, power management capabilities, and comprehensive software functionality.
Nigerian businesses should prioritize devices offering universal SIM compatibility, multi-band cellular support, and robust offline operation capabilities. These features ensure reliable connectivity across diverse network conditions while maintaining operational continuity during infrastructure challenges common in African markets.
Implementation success depends on systematic evaluation using the criteria outlined in this guide, combined with thorough vendor assessment and pilot testing in actual deployment environments. Starting with limited pilot deployments allows validation of device performance before large-scale implementation.
Ready to identify and deploy the right IoT devices for your Nigerian business? Contact Genyz Solutions today for expert consultation on device selection, connectivity solutions, and deployment strategies tailored to your specific industry requirements. Our team of African IoT specialists will help you navigate device selection complexities while ensuring optimal performance and ROI across your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the most important hardware specifications for IoT devices in Nigerian environments? A: Essential specifications include multi-band cellular support (900/1800/2100/2600 MHz), IP65+ environmental protection, wide temperature tolerance (0-60°C), low power consumption (<5W), battery backup (8-12 hours), and dual-SIM capabilities for network redundancy across Nigerian carriers.
Q: How do I ensure IoT devices work with Nigerian network operators? A: Look for devices with NCC type approval, multi-band cellular modems supporting MTN/Airtel/Glo/9mobile frequencies, universal SIM compatibility, and automatic carrier switching capabilities. Test devices with your intended roaming SIMs before large-scale deployment.
Q: What software features are essential for African IoT deployments? A: Critical software features include offline data storage, over-the-air updates, end-to-end encryption, multi-protocol support (MQTT, HTTP, CoAP), API accessibility, and intelligent connectivity management for handling intermittent network coverage common in African infrastructure.
Q: How do I calculate the total cost of ownership for IoT devices in Nigeria? A: Include device purchase price in Naira, connectivity costs, power consumption expenses, maintenance requirements, expected lifespan (5+ years), support costs, and potential currency fluctuation impacts. Quality devices often provide better long-term ROI despite higher upfront costs.
Q: What certifications should I look for in IoT devices for Nigerian deployment? A: Essential certifications include NCC type approval for Nigerian operation, FCC/CE marks for international standards compliance, IP rating for environmental protection, and industry-specific certifications (banking, healthcare, etc.) based on your application requirements.
Q: How can I future-proof my IoT device selection for emerging technologies? A: Choose devices with modular designs, 5G upgrade paths, sufficient processing power for edge computing, over-the-air update capabilities, and manufacturers with strong track records for long-term support and compliance with evolving African regulatory requirements.