Introduction
IoT security has become a critical concern for Nigerian enterprises. Cybersecurity threats targeting IoT devices increased 67% year-over-year globally. Moreover, manufacturing and energy sectors face the highest attack rates. Specifically, accounting for over 40% of IoT malware attacks. Additionally, mobile devices provide entry points into corporate networks. Therefore, comprehensive security strategies prove essential.
For Nigerian businesses deploying IoT projects, security considerations determine success or failure. Specifically, protecting banking systems like those at FCMB and Wema Bank. Moreover, securing industrial operations. Additionally, safeguarding logistics networks. However, effective protection requires more than firewalls. Therefore, zero-trust architectures combined with secure connectivity prove necessary. Particularly through protected universal SIM cards.
This comprehensive guide examines IoT security challenges facing Nigerian enterprises. Moreover, it explores emerging threat patterns. Additionally, it reveals protection strategies. Furthermore, it provides implementation guidance. Whether you’re managing IoT deployments or planning security infrastructure, understanding these threats ensures your Nigerian operations remain protected against evolving cyber risks.
1. Understanding IoT Security Threats in Nigeria
IoT security threats evolve constantly. Moreover, they specifically target Nigerian enterprises. Additionally, understanding threat patterns enables effective protection. Therefore, businesses must recognize emerging risks.
Malware Targeting IoT Devices
Dominant Threat Families
Three malware families dominate IoT attacks globally. Specifically, Mirai, Mozi, and Gafgyt. Together, they account for approximately 75% of malicious IoT payloads. Moreover, they primarily target routers and gateways. Therefore, compromising network entry points.
These malware families exploit weak default credentials. Specifically, devices using factory passwords. Moreover, targeting unpatched vulnerabilities. Additionally, leveraging poor network segmentation. Therefore, gaining control of IoT devices easily.
For Nigerian businesses, these threats prove particularly dangerous. Specifically, many IoT deployments use default configurations. Moreover, firmware updates lag behind vulnerability disclosures. Additionally, network segmentation remains minimal. Therefore, creating exploitable weaknesses across enterprises.
Sector-Specific Attack Patterns
Industries Under Siege
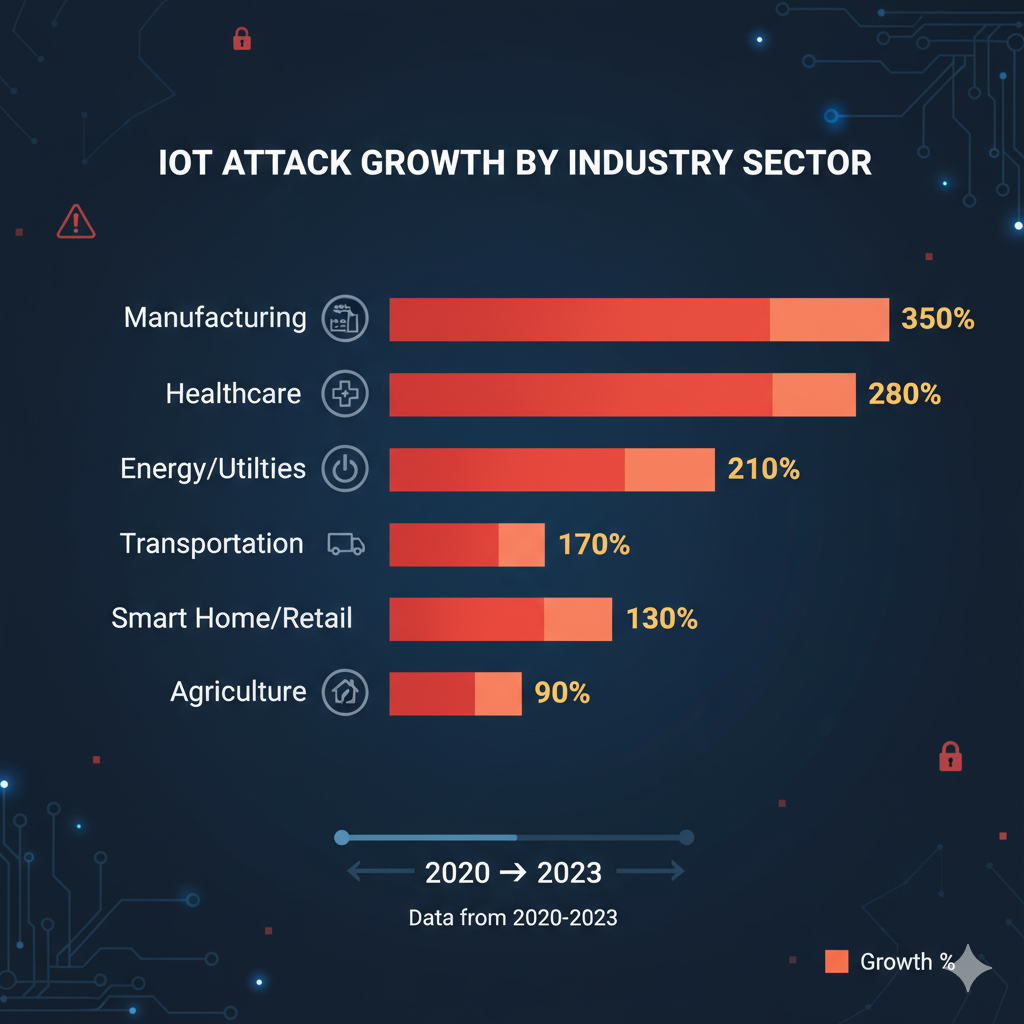
Manufacturing and transportation sectors face the highest attack rates. Specifically, each accounting for 20.2% of IoT malware attacks. Moreover, energy and utilities experience 459% year-over-year growth in attacks. Additionally, finance and insurance see 702% increases. Therefore, demonstrating accelerating threat levels.
Nigerian industries mirror these global patterns. For instance, manufacturing facilities in Lagos face constant probing. Additionally, energy infrastructure across Nigeria experiences targeted attacks. Moreover, banking IoT systems require continuous monitoring. Therefore, necessitating sector-specific security approaches.
The arts, media, and entertainment sector saw 1,862% attack growth. Similarly, education experienced 861% increases. Therefore, demonstrating no sector remains immune. Consequently, all Nigerian enterprises require robust IoT security regardless of industry.
Mobile Device Entry Points
The Weakest Link
Mobile devices provide easy entry into corporate networks. Specifically, through BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies. Moreover, employees access corporate resources via personal smartphones. Additionally, hybrid work increases mobile device dependency. Therefore, creating extensive attack surfaces.
Android malware transactions grew 67% year-over-year. Specifically, targeting trusted app marketplaces. For instance, 239 malicious apps achieved 42 million downloads. Moreover, using social engineering like SMS phishing. Therefore, tricking users into installing malware.
Nigerian businesses face similar mobile threats. Specifically, employees downloading compromised apps. Moreover, accessing corporate networks via infected devices. Additionally, granting excessive permissions unknowingly. Therefore, requiring mobile security strategies alongside IoT protection.
2. Cellular IoT Connectivity Security Challenges
Cellular IoT devices create unique security challenges. Specifically, for Nigerian deployments. Moreover, connectivity itself becomes a security concern. Therefore, requiring specialized protection strategies.
Shadow Attack Surfaces
Hidden Vulnerabilities
Cellular-connected IoT devices often operate remotely. Specifically, in rugged or isolated environments. Moreover, outside traditional network perimeters. Additionally, with limited physical security. Therefore, creating “shadow attack surfaces” difficult to detect and defend.
These devices typically lack security monitoring. Specifically, no intrusion detection systems. Moreover, minimal logging capabilities. Additionally, infrequent security updates. Therefore, remaining vulnerable for extended periods.
Nigerian agricultural IoT deployments particularly face these challenges. For instance, soil sensors across remote farms. Additionally, weather stations in isolated locations. Moreover, livestock trackers in grazing areas. Therefore, requiring connectivity security beyond traditional approaches.
SIM Card Vulnerabilities
Weak Protection Mechanisms
Traditional SIM cards provide minimal security protections. Specifically, easily cloned or compromised. Moreover, enabling unauthorized network access. Additionally, allowing data plan abuse. Therefore, creating security and cost risks.
Attackers target SIM cards for several reasons. First, gaining network access without physical device compromise. Second, intercepting communications. Third, using unlimited data plans maliciously. Fourth, hiding attack origins. Therefore, requiring SIM-level security measures.
Universal SIM cards from Genyz Solutions incorporate enhanced protections. Specifically, encrypted authentication. Moreover, tamper detection. Additionally, remote disabling capabilities. Therefore, addressing SIM-specific vulnerabilities effectively.
Network Coverage and Security Trade-offs
Connectivity Complexity
Nigerian IoT deployments require multinetwork connectivity. Specifically, switching between MTN, Airtel, Glo, and 9mobile. Moreover, ensuring continuous operation. However, network switching creates security considerations.
Each operator maintains different security postures. Specifically, varying encryption standards. Moreover, different authentication mechanisms. Additionally, inconsistent monitoring capabilities. Therefore, requiring security strategies accommodating multinetwork complexity.
Genyz Solutions’ universal SIM cards maintain security across networks. Specifically, consistent encryption regardless of operator. Moreover, unified authentication protocols. Additionally, centralized security monitoring. Therefore, eliminating multinetwork security gaps.
3. Zero-Trust Architecture for IoT Security
Traditional perimeter-based security proves inadequate for IoT. Instead, zero-trust architectures provide effective protection. Moreover, specifically addressing IoT characteristics. Therefore, Nigerian enterprises should adopt zero-trust approaches.
Core Zero-Trust Principles
Never Trust, Always Verify
Zero-trust assumes breaches will occur. Therefore, preventing lateral movement becomes critical. Specifically, limiting compromise impact. Moreover, containing threats quickly. Additionally, minimizing damage. Therefore, fundamentally different from perimeter defense.
Zero-trust requires three core capabilities. First, complete visibility into all devices. Second, granular access controls. Third, continuous verification. Therefore, ensuring only authorized activities occur.
For Nigerian IoT deployments, this means several things. Specifically, discovering all connected devices. Moreover, classifying by risk level. Additionally, segmenting networks appropriately. Furthermore, monitoring continuously. Therefore, maintaining security despite device compromise.
Network Segmentation Strategies
Isolating IoT Systems
Network segmentation prevents compromised devices from accessing critical systems. Specifically, creating isolated network zones. Moreover, controlling traffic between zones. Additionally, limiting broadcast domains. Therefore, containing security incidents.
Effective segmentation approaches include several strategies. First, separating IoT devices from corporate networks. Second, isolating different IoT device types. Third, creating “networks of one” for high-risk devices. Fourth, implementing micro-segmentation. Therefore, minimizing attack surface systematically.
Nigerian manufacturing facilities should implement strict segmentation. For instance, separating production IoT from corporate networks. Additionally, isolating industrial control systems. Moreover, segmenting by production line. Therefore, preventing factory-wide compromises from single device infections.
Continuous Monitoring and Verification
Real-Time Threat Detection
Zero-trust requires continuous monitoring. Specifically, analyzing device behavior constantly. Moreover, detecting anomalies quickly. Additionally, responding automatically. Therefore, identifying threats before significant damage.
Monitoring should track multiple indicators. For instance, traffic patterns. Additionally, connection attempts. Moreover, data volumes. Furthermore, unusual behaviors. Therefore, building baseline understanding and detecting deviations.
Genyz Solutions’ SIM management platform provides connectivity monitoring. Specifically, tracking device communications. Moreover, identifying unusual patterns. Additionally, alerting administrators. Therefore, enabling rapid threat response for Nigerian IoT deployments.
4. Securing IoT Connectivity in Nigerian Enterprises
Connectivity security forms the foundation of IoT protection. Specifically, for Nigerian deployments. Moreover, addressing unique African telecommunications challenges. Therefore, requiring specialized approaches.
Enhanced SIM Card Security
Beyond Basic Authentication
Traditional SIM security relies on simple authentication. However, advanced threats require enhanced protection. Specifically, encrypted communications. Moreover, mutual authentication. Additionally, tamper resistance. Therefore, going beyond standard SIM capabilities.
Secure SIM solutions incorporate multiple protections. First, cryptographic key storage. Second, secure elements preventing extraction. Third, remote management capabilities. Fourth, usage monitoring and alerts. Therefore, providing comprehensive SIM-level security.
Genyz Solutions offers security-enhanced universal SIM cards. Specifically, designed for enterprise IoT. Moreover, incorporating advanced protections. Additionally, supporting secure provisioning. Furthermore, enabling remote security management. Therefore, addressing Nigerian enterprise security requirements.
VPN and Encrypted Communications
Protecting Data in Transit
IoT data transmission requires protection. Specifically, preventing interception. Moreover, ensuring integrity. Additionally, maintaining confidentiality. Therefore, encryption becomes essential.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) connectivity provides secure channels. Specifically, encrypting all communications. Moreover, authenticating endpoints. Additionally, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks. Therefore, securing data across untrusted networks.
Nigerian banking IoT systems should mandate VPN connections. For instance, ATM monitoring data. Additionally, transaction processing. Moreover, customer information. Therefore, ensuring sensitive data remains protected despite network compromises.
Access Control and Authentication
Limiting Device Permissions
IoT devices should receive minimum necessary permissions. Specifically, following least-privilege principles. Moreover, restricting network access. Additionally, limiting API capabilities. Therefore, reducing compromise impact.
Strong authentication mechanisms prove essential. For instance, certificate-based authentication. Additionally, multi-factor authentication where feasible. Moreover, regular credential rotation. Therefore, preventing unauthorized access effectively.
Genyz Solutions’ connectivity platform supports granular access controls. Specifically, defining device permissions centrally. Moreover, enforcing policies across networks. Additionally, monitoring access attempts. Therefore, enabling secure Nigerian IoT deployments.
5. Practical IoT Security Implementation for Nigeria
Implementing IoT security requires systematic approaches. Moreover, addressing Nigerian infrastructure realities. Additionally, balancing security with operational requirements. Therefore, practical strategies prove essential.
Device Discovery and Inventory
Visibility as Foundation
Security begins with complete visibility. Specifically, discovering all connected IoT devices. Moreover, including managed, unmanaged, and shadow systems. Additionally, classifying by type and risk. Therefore, enabling appropriate security measures.
Discovery should identify several device characteristics. First, manufacturer and model. Second, firmware versions. Third, network connections. Fourth, communication patterns. Fifth, security capabilities. Therefore, building comprehensive device profiles.
Nigerian enterprises often discover unexpected IoT devices. For instance, employee-purchased smart devices. Additionally, legacy systems forgotten during migrations. Moreover, contractor-installed equipment. Therefore, systematic discovery reveals hidden risks requiring management.
Security Policy Development
Defining Protection Requirements
Clear security policies guide IoT protection. Specifically, defining acceptable use. Moreover, establishing security baselines. Additionally, specifying monitoring requirements. Furthermore, outlining incident response. Therefore, providing operational frameworks.
Policies should address multiple areas. First, device procurement requirements. Second, deployment procedures. Third, network connectivity rules. Fourth, data handling standards. Fifth, decommissioning processes. Therefore, covering complete IoT lifecycle.
Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) regulations require certain protections. Specifically, data privacy measures. Moreover, security incident reporting. Additionally, infrastructure resilience. Therefore, policies must address regulatory compliance alongside business requirements.
Incident Response Planning
Preparing for Breaches
Despite protections, security incidents occur. Therefore, response planning proves critical. Specifically, defining detection procedures. Moreover, establishing response teams. Additionally, documenting containment steps. Furthermore, planning recovery processes. Therefore, minimizing incident impact.
Response plans should address IoT-specific scenarios. For instance, compromised device discovery. Additionally, botnet infection detection. Moreover, data exfiltration attempts. Furthermore, denial-of-service attacks. Therefore, enabling rapid, effective responses.
Genyz Solutions provides incident support for connectivity-related security events. Specifically, assisting with compromised SIM identification. Moreover, remotely disabling affected connections. Additionally, analyzing attack patterns. Therefore, supporting Nigerian enterprise security operations.
6. Industry-Specific IoT Security Considerations
Different industries face unique IoT security challenges. Therefore, sector-specific strategies prove necessary. Moreover, addressing particular threats and requirements. Consequently, Nigerian enterprises should adopt tailored approaches.
Manufacturing and Industrial IoT
Operational Technology Protection
Manufacturing IoT connects operational technology (OT) with IT systems. Specifically, creating security challenges. Moreover, balancing security with production requirements. Additionally, protecting legacy systems. Therefore, requiring specialized approaches.
Industrial IoT security should emphasize availability. Specifically, ensuring production continues. Moreover, preventing safety system compromise. Additionally, protecting intellectual property. Therefore, prioritizing different concerns than traditional IT.
Nigerian manufacturing facilities should implement strict OT/IT segmentation. For instance, isolating production networks. Additionally, requiring VPN access for remote management. Moreover, monitoring for unusual control commands. Therefore, protecting critical operations.
Banking and Financial Services
High-Value Target Protection
Financial services IoT manages critical operations. Specifically, ATM networks. Moreover, branch security systems. Additionally, transaction processing. Therefore, requiring maximum security.
Banking IoT security demands several measures. First, encrypted communications. Second, strong authentication. Third, continuous monitoring. Fourth, rapid incident response. Fifth, regulatory compliance. Therefore, comprehensive protection strategies.
Genyz Solutions supports FCMB and Wema Bank IoT security. Specifically, providing secure connectivity. Moreover, monitoring for suspicious activity. Additionally, enabling rapid response. Therefore, protecting Nigerian financial infrastructure.
Energy and Utilities
Critical Infrastructure Protection
Energy sector IoT controls critical infrastructure. Specifically, power generation and distribution. Moreover, oil and gas operations. Additionally, water systems. Therefore, representing high-value targets.
Energy IoT security faces unique challenges. First, geographically distributed assets. Second, harsh environments. Third, long equipment lifecycles. Fourth, safety criticality. Therefore, requiring robust, long-term protection.
Nigerian energy infrastructure particularly needs security attention. For instance, remote pipeline monitoring. Additionally, offshore platform communications. Moreover, power grid management. Therefore, implementing defense-in-depth strategies across operations.
Agriculture and Logistics
Distributed System Security
Agricultural and logistics IoT operates across vast areas. Specifically, often remotely. Moreover, with limited physical security. Additionally, using cellular connectivity extensively. Therefore, requiring mobile-focused security.
These sectors should emphasize SIM security. Specifically, preventing unauthorized usage. Moreover, monitoring data consumption. Additionally, detecting anomalous communications. Therefore, leveraging connectivity-layer protections.
Genyz Solutions’ universal SIM cards provide security for distributed deployments. Specifically, tamper detection. Moreover, usage alerts. Additionally, remote disabling. Therefore, protecting Nigerian agricultural and logistics IoT effectively.
7. Future IoT Security Trends in Nigeria
IoT security continues evolving. Several trends particularly impact Nigerian enterprises. Moreover, requiring proactive preparation. Therefore, forward-looking businesses should anticipate developments.
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Intelligent Security Systems
Artificial intelligence enhances threat detection. Specifically, analyzing behavior patterns. Moreover, identifying anomalies automatically. Additionally, predicting attacks. Therefore, enabling proactive security.
AI security systems learn continuously. For instance, understanding normal device behaviors. Additionally, detecting subtle deviations. Moreover, correlating indicators across systems. Therefore, identifying sophisticated threats humans might miss.
Nigerian enterprises should evaluate AI security tools. Specifically, for large IoT deployments. Moreover, where manual monitoring proves impractical. Therefore, leveraging automation for comprehensive protection.
5G Security Implications
Next-Generation Connectivity Challenges
5G networks introduce new security considerations. Specifically, increased device density. Moreover, edge computing integration. Additionally, network slicing capabilities. Therefore, requiring updated security approaches.
5G also provides security improvements. For instance, enhanced encryption. Additionally, better authentication. Moreover, network function virtualization security. Therefore, offering both opportunities and challenges.
As 5G deploys across Nigerian cities, enterprises should update security strategies. Specifically, leveraging 5G security features. Moreover, addressing new attack surfaces. Therefore, maintaining protection through technology transitions.
Regulatory Evolution
Compliance Requirements
The Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) continues developing IoT regulations. Specifically, addressing security requirements. Moreover, data protection mandates. Additionally, critical infrastructure rules. Therefore, compliance requirements evolve.
Proactive businesses engage with regulatory development. Specifically, understanding emerging requirements. Moreover, implementing ahead of mandates. Therefore, avoiding compliance gaps and demonstrating leadership.
Zero-Trust Maturity
Advanced Implementation
Zero-trust adoption accelerates globally. Moreover, implementations become more sophisticated. Specifically, deeper segmentation. Additionally, finer-grained controls. Furthermore, automated responses. Therefore, raising security baselines.
Nigerian enterprises should plan zero-trust journeys. Specifically, starting with visibility. Subsequently, implementing segmentation. Moreover, adding continuous verification. Therefore, progressively enhancing security maturity.
Conclusion: Securing Nigerian IoT with Genyz Solutions
IoT security represents critical business priorities for Nigerian enterprises. Threats accelerate across sectors. Moreover, attack sophistication increases. Additionally, consequences grow more severe. Therefore, comprehensive protection strategies prove essential. Zero-trust architectures combined with secure connectivity provide effective defense.
Genyz Solutions enables secure Nigerian IoT through multiple capabilities. Specifically, security-enhanced universal SIM cards. Moreover, multinetwork connectivity maintaining protection. Additionally, SIM management platforms monitoring threats. Furthermore, expert security consulting. Therefore, comprehensive solutions addressing Nigerian enterprise requirements.
Our proven experience supporting FCMB, Wema Bank, and enterprises across Nigeria demonstrates security capabilities. Specifically, protecting mission-critical IoT deployments. Moreover, maintaining operations despite threats. Therefore, partnering with Genyz Solutions ensures your Nigerian IoT systems remain secure.
As cyber threats evolve and attack volumes increase, IoT security becomes non-negotiable. Organizations with robust security architectures and protected connectivity will maintain operations and customer trust. Meanwhile, those with inadequate security will face breaches, downtime, and reputation damage. Therefore, investing in IoT security and secure connectivity protects Nigerian business continuity and competitiveness.

